SQL (Ch 4)
Dr. Andrew Besmer
Account
Get an Account
To Connect
- Need to be on campus or connected to a campus server
mysql -h deltona.birdnest.org -u my.besmera2 -pTerms
DBMS vs Relational
- Table, row, and column instead of relation, tuple, and attribute
- Lot’s of people will still use these interchangeably
| Relational Model | DBMS |
|---|---|
| Relation | Table |
| Tuple | Row |
| Attribute | Column |
Schema
- SQL Schema
- A set of statements used to define elements in the database. Each statement terminates with a
;
- We can specify data definitions or schema’s using the
CREATEcommand - Elements include:
- Tables
- Constraints
- Views
- Domains
Schema
- Within a schema specify a new relation (now a table)
- Name
- Attributes
- Constraints
Catalog
- Catalog
- A named collection of schemas
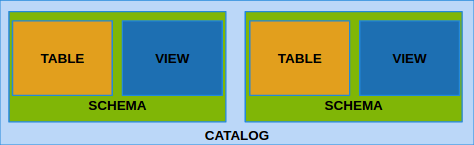
CREATE DATABASE my_besmera2; -- Catalog
CREATE TABLE Product (
name VARCHAR(255)
); -- SchemaData Types
Row Size
- 65,535 is the maximum row size in bytes for MyISAM
- Total length for all columns added together
- All varying columns also impact row size because they must store length
- Columns allowing NULL take up 1 bit extra each, must round up
BLOBandTEXTare stored separately from the row- Still have impact on row size since length must be stored
- More later
Integers
- Integer numbers:
TINYINT,SMALLINT,MEDIUMINT,INT,BIGINT
| Type | Bytes | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
TINYINT Signed |
1 | -128 | 127 |
TINYINT Unsigned |
0 | 255 | |
SMALLINT Signed |
2 | -32768 | 32767 |
Integers
| Type | Bytes | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
SMALLINT Unsigned |
0 | 65535 | |
MEDIUMINT Signed |
3 | -8388608 | 8388607 |
MEDIUMINT Unsigned |
0 | 16777215 | |
INT Signed |
4 | -2147483648 | 2147483647 |
Integers
| Type | Bytes | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
INT Unsigned |
0 | 4294967295 | |
BIGINT Signed |
8 | -9223372036 854775808 | 9223372036 854775807 |
BIGINT Unsigned |
0 | 1844674407 3709551615 |
Integers
- Can set display width by setting value, i.e.
SMALLINT(4) BOOLEANis reallyTINYINT(1)
Floats
- Floating point (real) numbers:
FLOAT,DOUBLEFLOATuses 4 bytes,DOUBLEuses 8 bytes- WARNING: These data types are approximations!
INSERT INTO DecimalTest VALUES (.1),(.7);
SELECT floor(sum(val)*10) FROM DecimalTest;Decimals
- Use
DECIMALwhen you want exact precision- Specify precision (
M) and scale (D)M- Max digitsD- Decimals
DECIMAL(M,D)whereMin{1,2,3,...,254}&Din{0,1,2,...30}Dmust never exceedMDECIMALis the sameDECIMAL(10,0)- Try testing
DOUBLEagainstDECIMAL
- Specify precision (
Decimal Storage
- Must calculate based on each side 9 digits at a time
| Digits | Bytes |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1–2 | 1 |
| 3–4 | 2 |
| 5–6 | 3 |
| 7–9 | 4 |
Time
DATE- 3 bytes- YYYY-MM-DD
- 1000-01-01 to 9999-12-31
DATETIME- 8 bytes- YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS[.fraction]
- Fractional seconds up to six digits
- Similar range as above
TIMESTAMP- 4 bytes- Based on UNIX epoch at 1970-01-01 00:00:01
- Range ends on 2038-01-19 @ 03:14:07
- Also has fractional precision
- Based on UTC and recorded in seconds since the epoch
Text
CHAR(M)Mis number of charactersMin{0,1,2,...,255}
- Space padded, see example.
VARCHAR(M)- For ASCII (1B)
Min{0,1,2,...,65535} - For UTF-8 (3B)
Min{0,1,2,...,21844}
- For ASCII (1B)
- Example calculations
Binary
BINARY(M)Mis number of bytesMin{0,1,2,...,255}
VARBINARY(M)Min{0,1,2,...,65535}
Text & Blob
- Contributes 9-12B toward total row size
- 8B + Length Bytes
| BLOB | TEXT | Length Bytes | Max Size? |
|---|---|---|---|
TINYBLOB |
TINYTEXT |
1 | ? |
MEDIUMBLOB |
MEDIUMTEXT |
3 | ? |
LONGBLOB |
LONGTEXT |
4 | ? |
BLOB(M) |
TEXT(M) |
Min Needed | ? |
Row Size
- Calculating total row size
- If we used
MEDIUMBLOB NOT NULLhow big of aVARCHAR(M) NOT NULLcould we store?VARCHAR(M) NULL?
- Calculate row size for table
- If we used
Constraints
Domains
- Domain
- Custom specification of data type to be used by multiple attributes.
- Domains increase schema readability
- MySQL does not support this
CREATE DOMAIN SSN_TYPE AS CHAR(9);Basic
- Key and referential constraints
FOREIGN KEY,PRIMARY KEY,UNIQUE KEY
- Restrictions on the attribute domain
NOT NULLCHAR(9)
- Default values
DEFAULT <value>
Check
CHECKclause- Constraints on individual rows (tuples) within a table (relation)
CHECKis not supported in MySQL
CHECK (Dnumber > 0 AND Dnumber < 21)Key
PRIMARY KEYclause- Specifies one or more attributes that makeup the primary key for the table
- Implicitly says
NOT NULL
UNIQUEclause- Specifies alternate keys
- NULLs are allowed on this attribute unless you specify
NOT NULL
Dnumber INT PRIMARY KEY -- as part of attribute optionsDname VARCHAR(15) UNIQUE -- as part of attribute optionsPRIMARY KEY (Dnumber) -- as part of table optionsUNIQUE KEY (Dname) -- as part of table optionsKeys
FOREIGN KEYclause- Default operation is reject when violated
- Must provide
REFERENCES - Can attach referential triggered action to
ON DELETEorON UPDATESET NULL,CASCADE,RESTRICTandSET DEFAULT
FOREIGN KEY (super_ssn) REFERENCES Employee(ssn) -- as part of table optionsCreation
Create Syntax
CREATE TABLE tbl_name
( col_name1 TYPE [options],
col_name2 TYPE [options],
...
col_nameN TYPE [options],
PRIMARY KEY(col_Name),
FOREIGN KEY (col2_name) REFERENCES tbl2_name(other_col_name)
); [table_options] -- Note FK can reference same table too!Create Table
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE
(
Fname VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
Minit CHAR(1),
Lname VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
Ssn CHAR(9) NOT NULL,
Bdate DATE,
Address VARCHAR(30),
Sex CHAR(1),
Salary DECIMAL(10,2),
Super_ssn CHAR(9),
Dno INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Ssn),
FOREIGN KEY (Super_ssn) REFERENCES EMPLOYEE(Ssn),
FOREIGN KEY (Dno) REFERENCES DEPARTMENT(Dnumber)
);
CREATE TABLE DEPARTMENT
(
Dname VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
Dnumber INT NOT NULL,
Mgr_ssn CHAR(9) NOT NULL,
Mgr_start_date DATE,
PRIMARY KEY (Dnumber),
UNIQUE (Dname),
FOREIGN KEY (Mgr_ssn) REFERENCES EMPLOYEE(Ssn)
);Chicken Egg
- Some FK’s may cause errors when creating tables
- How can you fix?
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD FOREIGN KEY (col_name) REFERENCES other_tbl(other_col);- In DBMS that follow SQL standards use
START TRANSACTION;
CREATE ...
CREATE ...
COMMIT;
Chicken Egg
- Same applies for rows, see
EMPLOYEE.DnoandDEPARTMENT.Mgr_ssn
Deviation from SQL standards: … InnoDB checks foreign key constraints immediately; the check is not deferred to transaction commit. According to the SQL standard, the default behavior should be deferred checking. That is, constraints are only checked after the entire SQL statement has been processed. Until InnoDB implements deferred constraint checking, some things will be impossible, such as deleting a record that refers to itself using a foreign key.
Insertion
Insert
- Insert data using the
INSERTstatement- If using
VALUESonly syntax you MUST specify a value for every column, in order- Recall ordered list of values
- Alternatively can supply the column or attribute names
- Forms the ordered pair across
VALUES
- Forms the ordered pair across
- If using
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...);
-- OR
INSERT INTO table_name (column1,column2,column3,...) VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...);Practice
- Lets create a
Producttable with:namequantityprice
- Row size?
- Then fill it with some data
Practice Result
CREATE TABLE Product (
name VARCHAR(200) PRIMARY KEY,
quantity SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
price DECIMAL(6,2) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO Product VALUES ("M&M's", 1000, .99);
INSERT INTO Product VALUES ("Mike&Ike", 500, 1.10), ("Diet Coke", 50, 2.00);
INSERT INTO Product (name, price) VALUES ("Popcorn", 2.99);
INSERT INTO Product (price, name) VALUES (99.99, "TI 93 Calculator"), (20.00, "T-Shirt");
INSERT INTO Product VALUES ("Frozen Pizza", 20, 7.99), ("Mini Toolkit", 20, 15.00), ("Flashlight" , 75 , 5.99 );
SELECT * FROM Product;
Retrieval
Selection
SELECT- Basic statement used to retreive data from DBMS.
SELECT <projection attributes> FROM <tables> WHERE <selection conditions> ORDER BY <attribute list>;
- Projection attributes
- The attribute names whose values will be retrieved by the query. A
*indicates all.
- Selection condition
- Boolean expression using relational and logical operators to conditionally return rows retrieved by the query.
Comparison
- Relational Comparison Operators
=- note the lack of a double equals<,<=,>,>=, and<>
- Logical Operators
AND,OR,NOT- More on
NOTlater
Comparison/Arithmetic
LIKEcomparison operator- Used for string pattern matching
%replaces an arbitrary number of zero or more characters_replaces a single character
- Standard arithmetic operators
- Addition
+, subtraction–, multiplication*, and division/
- Addition
- BETWEEN comparison operator
WHERE DNumber BETWEEN 1 AND 2
Order
- DBMS will make no guarantee of the order without an
ORDER BYclause- Can order
ASCfor ascending orDESCfor descending - Can provide multiple attributes to sort on
- Can order
SELECT name FROM Product WHERE price > 2 ORDER BY price DESC, name ASC;Duplicates
- SQL does not automatically eliminate duplicate rows
- Use keyword
DISTINCTwith aSELECT
SELECT salary FROM EMPLOYEE;
SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM EMPLOYEE; Views
- Virtual tables can be created as a view
CREATE VIEW ProductValues AS SELECT qty*price AS value FROM Product;Conceptual Steps
- Iterate over each row
- Check selection condition
- Order rows
- Project attributes/columns
SELECT name FROM Product WHERE price > 2 ORDER BY price;Useful Commands Before Practice
- Create a database
- Show the databases
- Show the tables in a database
- Show a tables schema
Practice
- What are all the products?
- Which products have a price greater than or equal to 10.00?
- Which products are not priced at .99?
- Which products are priced at .99?
- Which products are between 5.00 and 10.00?
- Which products are less than 5.00 or greater than 10.00?
- Which products are out of stock?
- In terms of value, which product on our shelves has the most?
Modification
UPDATE
UPDATESyntax
UPDATE table SET col1=val1, col2=val2 WHERE col3=val3;- WARNING: Failure to include a WHERE clause will cause it to operate on all rows!!!!
DELETE
DELETESyntax
DELETE FROM table WHERE col1=val1;- WARNING: Failure to include a WHERE clause will cause it to operate on all rows!!!!
Multiple Tables
Selection
- When selecting from multiple tables you must
JOINthem - Types of JOINS
CROSS JOIN- Cartesian product- INNER - Implicit vs Explicit
- EQUI & NON-EQUI
INNER JOINorJOIN
- NATURAL
NATURAL JOIN
- EQUI & NON-EQUI
- OUTER
LEFT JOINRIGHT JOINFULL JOIN1
JOIN PDF
- Refer to
JOINPDF
Ambiguous Attributes
- Same name can be used for two or more attributes (in different relations/tables)
- When selecting must qualify the attribute name with relation name
EMPLOYEE.Dnumber
SELECT Fname, EMPLOYEE.Name, Address FROM EMPLOYEE JOIN DEPARTMENT ON DEPARTMENT.Dnumber = EMPLOYEE.Dnumber WHERE DEPARTMENT.Name = 'Research' ;
-- or
-- NOT ADVISED TO DO:
SELECT Fname, EMPLOYEE.Name, Address FROM EMPLOYEE, DEPARTMENT WHERE DEPARTMENT.Name = 'Research' AND DEPARTMENT.Dnumber = EMPLOYEE.Dnumber;Aliasing
- Alias using the AS keyword
EMPLOYEE AS E(Fn, Mi, Ln, Ssn, Bd, Addr, Sex, Sal, Sssn, Dno)
-- Now can use Select E.Fn, E.Ln .....
-- MySQL Ex: Select C.id AS i, C.Name AS n FROM Company AS C;ER Diagram
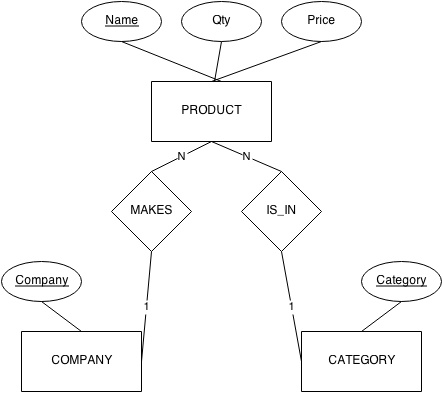
- Convert to Relations
Pure Relations
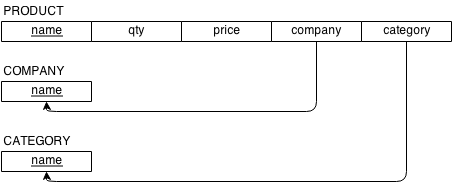
- Make SQL
CREATE TABLE - Calculate Row Sizes
Sensible Relations
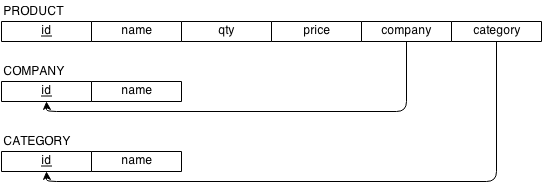
- Make SQL
CREATE TABLE - Calculate Row Sizes
SQL
-- DROP Existing
DROP VIEW ProductValues;
DROP TABLE Product, Company, Category;
-- Create Product Table
CREATE TABLE Product (
id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
qty SMALLINT NOT NULL,
price DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL,
company SMALLINT UNSIGNED default NULL,
category SMALLINT UNSIGNED default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ;
-- Create Category Table
CREATE TABLE Category (
id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ;
-- Add Category Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE Product ADD FOREIGN KEY (category) REFERENCES Category(id);
-- Create Company Table
CREATE TABLE Company (
id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB ;
-- Add Company Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE Product ADD FOREIGN KEY (Company) REFERENCES Company(id);
-- Fill Category Table
INSERT INTO Category (name) VALUES ("Toys"), ("Tools"), ("Health");
-- Fill Company Table
Insert INTO Company (name) VALUES ("LEGO"), ("Craftsman"), ("Stanley"), ("Crest");
-- Fill Product Table
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Batman Lego Set", Category.id, Company.id, 1, 9.99 from Category, Company WHERE Category.name = "Toys" AND Company.name = "LEGO";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "32 Piece Ratchet Set", Category.id, Company.id, 2, 29.99 from Category, Company WHERE Category.name = "Tools" AND Company.name = "Stanley";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Hammer", Category.id, Company.id, 5, 5.99 from Category, Company WHERE Category.name = "Tools" AND Company.name = "Stanley";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Toothpaste", Category.id, Company.id, 1, 2.99 from Category, Company WHERE Category.name = "Health" AND Company.name = "Crest";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Floss", Category.id, Company.id, 3, .99 from Category, Company WHERE Category.name = "Health" AND Company.name = "Crest";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Power Drill", Category.id, NULL, 5, 49.99 from Category WHERE Category.name = "Tools";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "120 Piece Lego Set", NULL, Company.id, 1, 12.99 from Company WHERE Company.name = "LEGO";
Insert INTO Product (name, category, company, qty, price) Select "Hot-wheels Car", NULL, NULL, 10, .99 ;
JOIN Practice
- Create a view showing the id, name of the product, and values of the product on hand (qty x price).
- Select the product name and the category name of all the products that actually have categories.
- Select the product name and the category name of all the products. (Even if they do not have categories.)
JOIN Practice
- Select all the products, the categories they belong to, and the company the product is made by. Hint: LEFT LEFT!
- Update the company Stanley to Stanley Black and Decker and rerun
- Select all the products in the tools category with a price greater than 10.00.
- Now only those made by Stanley Black and Decker.
JOIN Practice
- Delete the LEGO company.
- What happened? Why?
- What can you do? Do it! Try again.
M:N JOIN Twitter

M:N JOIN Twitter

M:N JOIN Twitter
DROP TABLE Follow, Tweet, User;
CREATE TABLE User (
id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE Tweet (
id BIGINT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
text VARCHAR(140) NOT NULL,
user INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
createdAt TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (user) REFERENCES User(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
);
CREATE TABLE Follow (
follower INT UNSIGNED,
followee INT UNSIGNED,
PRIMARY KEY(follower, followee),
FOREIGN KEY (follower) REFERENCES User(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (followee) REFERENCES User(id) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
);
INSERT INTO User (name) VALUES ("KATY PERRY"),("Justin Bieber"),("Elon Musk"),("Taylor Swift"),("YouTube"),("Rihanna"),("Lady Gaga"),("Justin Timberlake"),("Ariana Grande");
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "If people want a role model, they can have Miley Cyrus!", id FROM User where name = "KATY PERRY";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "My personality is up and down, sassy and cheeky.", id FROM User where name = "KATY PERRY";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Canada's the best country in the world.", id FROM User where name = "Justin Bieber";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I want to give people a taste of the Caribbean, and show them the fun side of me.", id FROM User where name = "Rihanna";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Love is like a brick. You can build a house, or you can sink a dead body.", id FROM User where name = "Lady Gaga";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "They can't scare me, if I scare them first.", id FROM User where name = "Lady Gaga";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Tesla stock price is too high imo", id FROM User where name = "Elon Musk";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I am selling almost all physical possessions. Will own no house.", id FROM User where name = "Elon Musk";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Just be yourself, there is no one better.", id FROM User where name = "Taylor Swift";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "No matter what happens in life, be good to people. Being good to people is a wonderful legacy to leave behind.", id FROM User where name = "Taylor Swift";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Want your video posted, send us a message!", id FROM User where name = "YouTube";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I never know what day it is. Never, ever, ever.", id FROM User where name = "Rihanna";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I like simple things. I like to sneak in the theatre and watch movies. I'm a movie buff.", id FROM User where name = "Justin Timberlake";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "Hello YouTubes!", id FROM User where name = "YouTube";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I try to read all of my fan mail. A lot of them send me candy, which I'm not allowed to eat 'cause my mom says it might be poisonous.", id FROM User where name = "Justin Bieber";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "I have 20,000 girlfriends, all around the world.", id FROM User where name = "Justin Timberlake";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "had the weirdest, scariest, most bizarre dreams ever last night. wow. One of them was me trapped in a room with Kevin Jonas and an alien.", id FROM User where name = "Ariana Grande";
SELECT SLEEP(1);
INSERT INTO Tweet (text, user) SELECT "who ariane", id FROM User where name = "Ariana Grande";
M:N JOIN Twitter
Insert data into
Followfor who Elon should be following. Remember he is incredibly busy so don’t add everyone. Also recall that the twitter relationship is not reciprocal.Write the SQL statement that would be necessary to display the twitter feed for Elon Musk. Recall that order is not guaranteed.
M:N JOIN Twitter
Add a
Tweetfor someone who you had Elon Musk follow and someone who he did not follow.Rerun your SQL statement to show the twitter feed. How many new Tweets did you see?